Submitted by ManuelRothe
on Tue, 12/03/2019 - 15:07
Water points must be included in any risk assessment and preparedness plan. When building or reinforcing resilient water points to ensure access to potable water the aftermath of a disaster and emergencies, consider these accessibility measures to ensure their safe use by everyone:
- The platform around water points should preferably use concrete base for safer mobility of wheelchair users or older persons, avoid slippery surface and ensure good drainage. Avoid gravel, bricks or other uneven surfaces.
- Level platforms with the surrounding ground. Alternatively, construction of a ramp at least 90 cm wide and with a gradient of at least 1:10. The nearer users can get to the water source, the easier it is to use
- Build a seat in front of the tap, at a height of 50 cm for sitting while collecting water (wood, concrete or metal can be used for this purpose). Install a small handrail beside the seat at a height of 90 cm.
- Install easy to use hand pumps for tube wells, with long handles and low resistance when pumping. In case a tap is installed on a water tank, the tap height should be 90cm.
- In case of lifting devices, using a ratchet and pawl will allow a winding and locking mechanism for the rope
- Build water points close to people’s homes/settlements for easier access.
- Involve community members, including women and men of different ages, with different types of disabilities in the planning and design of the location, specifications and resources for installation water points.
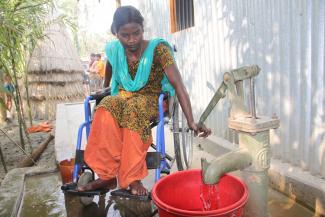
© CDD 2015
In case of an open well, without lifting mechanism, several arrangements on the raised wall facilitate access to persons with disabilities, elderly and young persons:
- Plan for a wall of different heights: the height of the wall should be between an adult's hip and waist (approximately 80cm high). It should be strong enough to support the weight of a person leaning on it while getting the water from the well. For a wheelchair user or a person sitting next to the wall, the wall should not be above the height of their waist or armrest (approximately 50cm high).
- A flat cover of the wall (wood or concrete) with an access hatch will provide additional surface to lean on and to rest the water container. In addition, it will reduce the risk of water contamination and the risk of accidents.
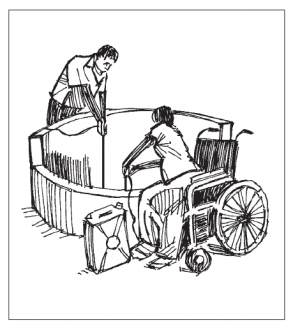
© Hazel Jones and Bob Reed. 2005
Sources
Ageing and Disability Task Force Pakistan. Technical Guidelines for Health, Water & Sanitation, Hygiene and Shelter Programmes in Emergencies.